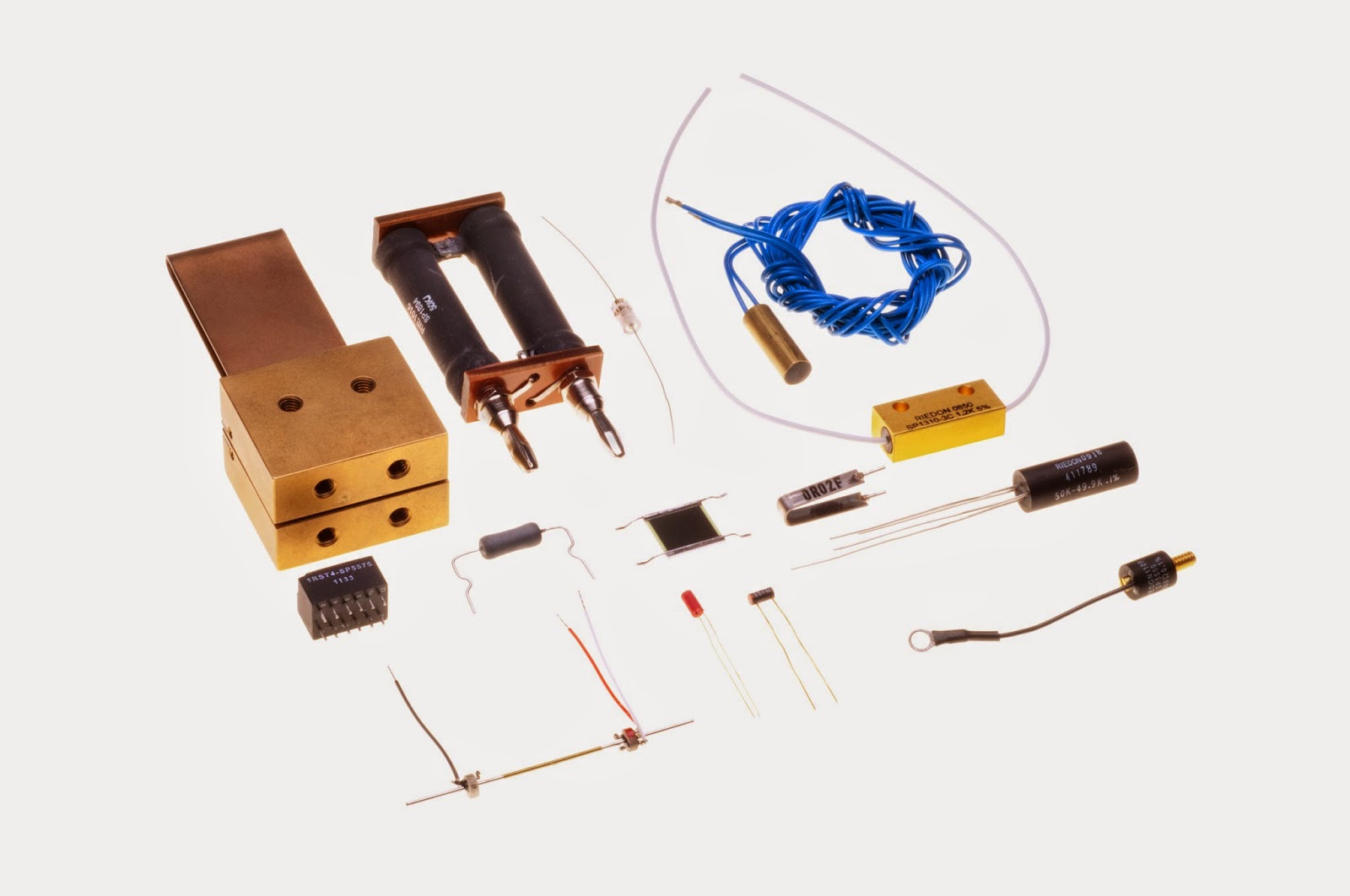
Wirewound resistors have been electrical passive components which limit current with the wire material featuring high resistivity. Their resistive elements exist out of the metallic wire insulated that has been winded around the non-conductive material core.The resistive elements are existing out of metal wire that is insulated and winded around a non-conductive core material. These resistors are usually made up of copper-nickel-manganese which is called as “Manganin” or nickel-chromium (Nichrome) materials. The wire wound resistors have been the oldest resistors kinds that have been manufactured in the present. They could be produced highly accurate and got a very excellent properties of high power rating and low resistance value.
The construction of a wire wound resistor varies to certain factors which involve the choice and manufacturing of material used depends on how the resistor is used in the circuit. The values of resistance rely on wire resistivity. It also involves cross section and length. For higher tolerance measurement, resistance value must be measured. This is to identify the accurate cut for the wire length. To make the resistance high, the diameter of the wire should be small enough while its length must be long.

Wirewound resistors have been giving capacitance and inductance that are affecting the current flow in an alternative current circuit. Because of the design principles of a wire wound resistor, this obtain poor frequency properties in all resistor types. There were distinct ways to apply winding and these rely on the application of the resistor. Through the DC current, there will only be a few problems in terms of winding compared to the AC current due to the self induction and parasitic capacity. In order to reduce the effects, there have been various kinds of winding that exist and these are the Ayrton-Perry winding, winding on the flat former and bifilar winding.
Types of winding are usually associated measurement devices as well as decade banks. However, the downside is more on difficult process of manufacturing. Wirewound resistors come in distinct kinds. They were categorized into power type and the precision type. These are being modified for distinct ranges of applications in temperature sensors, potentiometers and current.
The wire resistor has been generally present in a fuse or in the circuit breaker. In order to come up with fusible resistors, the manufacturers are going to integrate small springs into the other end of a resistor. When the heat and current through the resistors become high enough, solders are going to melt while the springs pop up as the circuit opens.